




The combination of advanced technologies has enabled a new system of agriculture known
as 'precision farming'.
This involves using technology to closely observe the performance of a crop, the farm
and its environment,
enabling farmers to carry out the appropriate actions in the right place at the right
time.
Measurements
Many different are measured on farms today. Some of the most important variables are:
- weather conditions - including temperature, humidity, rainfall and light levels.
- soil conditions - including temperature, , nutrient and moisture levels.
- crop status - including development and health problems (such as disease or nutrient deficiencies).
Technologies
All of the technologies that we've looked at play a part in precision farming.
Satellites, drones and sensors closely observe farms and measure variables.
Today, information can be quickly transferred to precision machinery, allowing for accurate planting, watering, crop protection and . In the future, autonomous vehicles and drones may be programmed to act on this information without human control.
All of the farmer's actions and results are recorded. This data can help the farmer improve their farming methods and can be shared with other farmers, scientists, plant breeders and engineers through information networks, helping the agricultural community to stay up to date with the best practices and latest innovations.
Thanks to this, farming practices are now advancing faster than ever before.
Impact
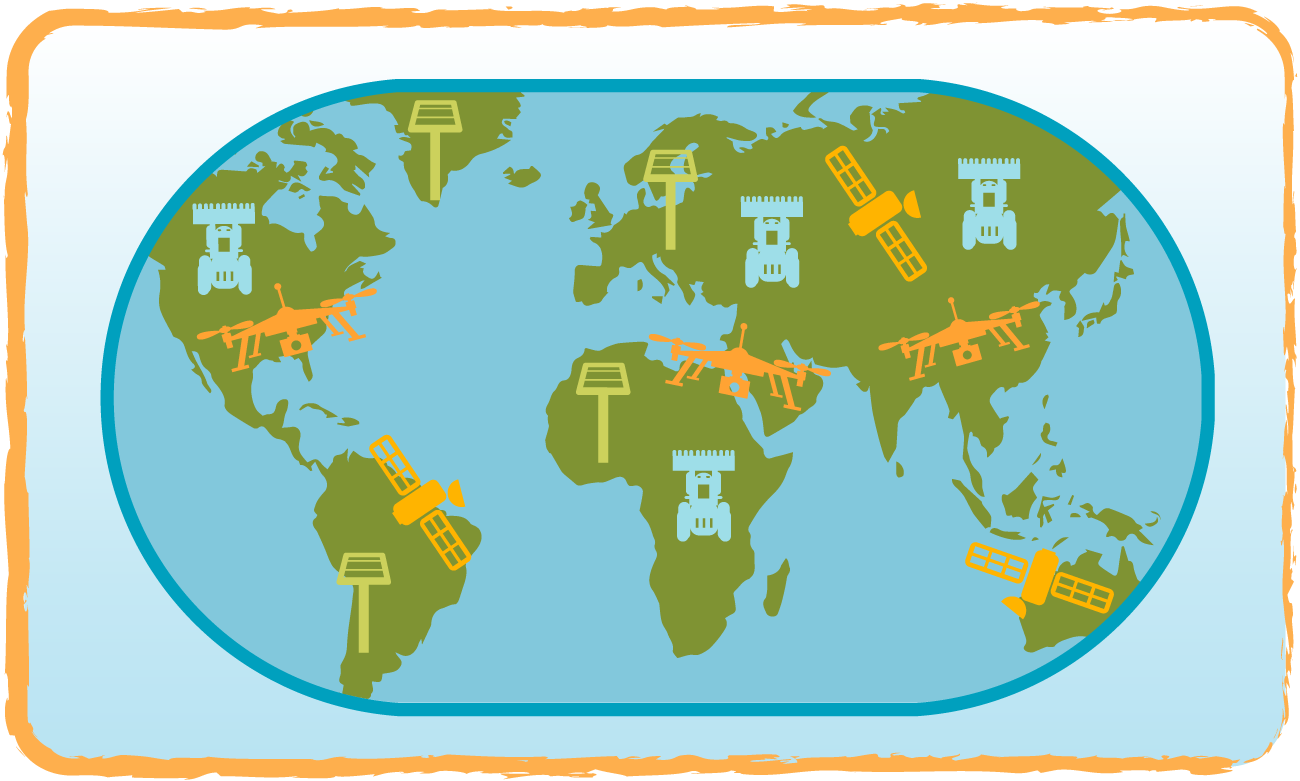
Elements of precision farming can be found all over the globe.
By using precision farming, farmers are able to increase the productivity of their farms.
They are able to precisely target their actions to the parts of their farms where they will have the most impact.
This can reduce the volume of fertilisers and crop protection chemicals being used,
limiting waste and the impact farming has on the environment.
Precision agriculture is mostly used in developed countries where farmers have the money to invest in machinery and digital technologies. Precision farming techniques could have a significant impact in developing countries in Africa, Asia and South America, but many of the farmers in these countries are and cannot afford the advanced technology.

